Can Dehydration Cause Erectile Dysfunction- Understanding the Connection

Erectile dysfunction is a common condition that affects millions of men worldwide, often causing frustration and impacting their quality of life. While many factors contribute to ED, dehydration is one surprisingly overlooked cause. Hydrating is essential for body function, but many don’t realize how important it is for sexual performance. Understanding the connection between dehydration and erectile dysfunction is crucial, as it highlights the importance of maintaining proper hydration not just for overall health but also for sexual well-being.
This article explores the science behind hydration and erectile health and ways to prevent dehydration-related ED.
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual activity. While it is normal for men to occasionally experience difficulty with erections, frequent or persistent issues can signal ED [1]. Suffering from the symptoms of erectile dysfunction may affect self-esteem, relationships, and overall well-being. ED becomes more common with age, but it is not a natural part of aging and can occur at any stage of life.
Importance Of Staying Hydrated For Overall Wellness
Hydration is vital for nearly every bodily function. Water makes up about 60% of the human body and is essential for regulating temperature, aiding digestion, lubricating joints, and ensuring proper cellular function. The body cannot perform optimally without adequate hydration, leading to various health issues [2].
Understanding The Relation Between Hydration and Erection
Erections rely on proper blood flow, regulated by the brain, nerves, and cardiovascular system. Hydration is essential for maintaining all the mentioned body functions, blood volume and circulation. When dehydrated, blood flow can be reduced, impacting erectile function.
Proper hydration also influences hormone production, including those responsible for sexual function, like testosterone.
Hydration And Muscle Relaxation For Better Blood Flow
Staying hydrated and keeping muscles relaxed are essential for optimal blood flow. Proper hydration supports smooth circulation, while muscle relaxation helps dilate blood vessels and reduces tension-related constriction, improving overall circulation.
Fact To KnowExcessive hydration in patients undergoing hemodialysis has been linked to a higher occurrence of sexual dysfunction and depression. Additionally, it was associated with reduced serum levels of total testosterone [4]. |
How Can Dehydration Impact Sexual Performance?
Dehydration can negatively affect sexual performance in several ways, primarily by interfering with the body’s ability to function efficiently. When the body lacks sufficient water, several processes essential for sexual health are disrupted, leading to issues like erectile dysfunction. Even slight dehydration can hinder sexual performance by causing fatigue, poor concentration, and mood swings [3].
A study in the Journal of Sexual Medicine revealed a correlation between dehydration and an increased likelihood of erectile dysfunction in men. Similarly, research from the University of Texas found that even mild dehydration can negatively affect sexual performance [5].
Here are a few factors that relate dehydration and erectile dysfunction together.
The Link Between Blood Circulation, Hydration, And Erections
One of the most direct ways dehydration impacts sexual performance is by reducing blood pressure [6]. This reduction leads to poorer circulation, making it more difficult for enough blood to reach the penis. Without proper blood flow, erections may be weaker or shorter-lasting.
Decreased Energy Levels
The hydration level can also affect sexual health by maintaining energy levels. When dehydrated, men often experience fatigue and lethargy, reducing stamina. Low energy can make it difficult to perform sexually.
Hormonal Imbalance
Dehydration can also affect the production of hormones like testosterone, which is vital for libido and sexual performance. Even mild dehydration may cause temporary drops in hormone levels, potentially lowering sexual desire and performance.
Studies further suggest that mild dehydration can trigger the release of cortisol, a hormone associated with stress. Elevated cortisol levels can have several physiological effects, including reduced testosterone production.
Mood Disorder
The connection between mood and erectile function is often overlooked, even though achieving an erection involves both physical and psychological components. Research suggests that even mild dehydration can cause anxiety, tension, and irritability in men. Emotional states such as sadness or lethargy can significantly impair sexual function, reducing the ability to become aroused, achieve an erection, or reach orgasm [7].
Signs You May Be Dehydrated
Here are common signs you may be dehydrated:

- Thirst: This is one of the most obvious signs that you are already dehydrated.
- Dark Urine: A darker, more concentrated urine is a key indicator of dehydration. Healthy hydration usually results in pale yellow urine.
- Dry Mouth and Skin: Dehydration can cause dry mouth, cracked lips, and dry or flaky skin.
- Fatigue: Lack of hydration can lower energy levels and fatigue, making you feel sluggish.
- Headaches: Dehydration often triggers headaches due to reduced fluid in the body, affecting blood flow to the brain.
- Dizziness: A drop in blood volume due to dehydration can cause dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Muscle Cramps: Dehydration can cause an imbalance in electrolytes, leading to muscle cramps or spasms.
- Bad Breath: Less saliva production can result in bacterial growth in the mouth, causing bad breath [8].
If you want to know about dehydration and its impact on the body, refer to the article on adult dehydration on NCBI.
Can Dehydration Cause Temporary Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, dehydration can cause temporary erectile dysfunction. Infact, dehydration and ED are correlated as when the body is dehydrated it decreases blood volume, leading to poor circulation, which can make it harder to achieve or maintain an erection. Drinking enough water may help improve circulation and reduce the risk of temporary ED.
Preventing Dehydration And Improving Sexual Health
Preventing dehydration and improving men’s sexual health go hand in hand, as staying hydrated supports overall bodily functions, including those crucial for sexual performance. Here are ways to prevent dehydration and boost sexual health:
- Get enough sleep
- Stay hydrated
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Exercise regularly to boost circulation
- Manage stress.
Best Drink For Erectile Dysfunction
Some of the best drinks for better erections and sexual health are listed below.
Beet juice
They are naturally rich in nitrates that the body converts to nitric oxide. This helps lower blood pressure and relax the blood vessels, thus improving blood circulation.
Watermelon juice
This is another excellent source of L-citrulline. They also help boost the body’s hydration level, thus allowing better circulation and managing erectile dysfunction.
Cucumber Drink For ED
The use of cucumbers for sexual health has recently gained attention. Apart from being rich in water and enhancing hydration levels, cucumber juice contains an amino acid called L-citrulline, which is converted into L-arginine in the body. The body uses this L-arginine to produce nitric oxide, which aids in relaxing the blood vessels and achieving an erection.
Proper Hydration And Semen Quality
Drinking enough water can enhance sperm quality, increase semen production, and improve your chances of conception.
Improves Sperm Quality
Dehydration and impotence are also correlated, as hydration impacts male fertility by improving sperm quality. Water is essential in the production of pre-ejaculate, a clear, lubricating fluid that is released from the penis before ejaculation. This fluid not only helps to lubricate but also neutralizes any acidity that could potentially harm sperm.
Enhances Sperm Motility
Drinking enough water can improve sperm motility, or the ability of sperm to swim efficiently. Motile sperm are essential for conception, as they must swim through the female reproductive tract to fertilize the egg.
Increases Semen Volume
Semen production is directly linked to your hydration levels. When you are well-hydrated, your body can produce the maximum amount of semen [9,10].
How Much Water Should You Drink For Sexual Health?
The U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine determined that men should have around 15.5 cups (3.7 liters) of water every day, whereas women should have around 11.5 cups (2.7 liters) of water [11].
To get a detailed understanding of daily water intake recommendations, check out Mayo Clinic’s guide on how much water you should drink every day.
When Water Isn’t Enough- Clinical Treatment Options
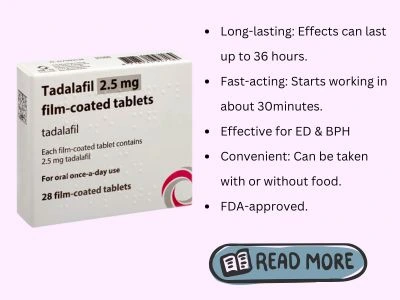
When dehydration leads to erectile dysfunction, medical treatments can help restore erectile function. Commonly prescribed medications include Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil.
Sildenafil Citrate
Sildenafil is a PDE5 inhibitor that helps improve blood flow to the penis by relaxing blood vessel muscles. It is widely used in erectile dysfunction treatment and starts working within 30 minutes of intake. The other options of the brand Viagra include Cenforce, Malegra, and Aurogra tablets. Among these, Cenforce tablets, manufactured by Centurion Laboratories in India, are among the most trusted choices for managing ED. For people looking for a higher dosage option, Cenforce 200mg ED medication offers stronger and long-lasting effects.
Key Benefits of Sildenafil
- Fast-acting: Sildenafil typically starts to work within 30 to 60 minutes.
- Proven efficacy: It can improve sexual function in men with ED, offering a reliable solution for many.
- Flexible timing: Its effects last up to 4 hours, giving you a window of opportunity for spontaneous intimacy.
- Simple to use: Taken orally in tablet form, Sildenafil is easy to incorporate into your routine.
- Widely trusted: Sildenafil has a long history of safe and effective use for treating ED.
Vardenafil
One of the key benefits of Vardenafil is its reliable performance, offering up to 4 to 6 hours of effectiveness, which provides flexibility for men. It can be taken with or without food, making it a convenient option for many users. Unlike some other ED treatments, Vardenafil is also known to cause fewer side effects for many men, which can improve overall user satisfaction. Vardenafil has a proven track record for safety and efficacy, making it a trusted choice for men looking to manage their erectile dysfunction.
Tadalafil
Can Dehydration Cause Erectile Dysfunction- Our Final Thought
While dehydration causes ED, it may not be the sole cause. It can certainly contribute to the condition by affecting blood flow, hormone balance, and overall energy levels. Staying properly hydrated is essential for maintaining general health and sexual function. If dehydration is impacting your ability to achieve or maintain an erection, simply rehydrating can help.
FAQs
Does drinking water help you sexually?
Can cold water cause erectile dysfunction?
Can drinking hot water for erectile dysfunction beneficial?
Can dehydration result in dehydrated cum?
Can Hot Weather Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Can dehydration affect ejaculation?
Can hot water cause erectile dysfunction?
Can dehydration-induced ED be reversed?
How do electrolyte imbalances impact sexual performance?
Can dehydration make you feel less aroused?
How fast does dehydration affect erectile function?
Does drinking coffee cause dehydration and ED?
How does dehydration affect nitric oxide and erections?
Does dehydration lower testosterone?
Can not drinking enough water cause erectile dysfunction?
Does water help erectile dysfunction?
References
- Erectile dysfunction - Symptoms and causes, MayoClinic.
- Why you need to drink water and stay hydrated, health.ucdavis.edu.
- The Vital Role of Hydration in Testosterone Replacement Therapy, trtnation.
- The relationship between hydration status, male sexual dysfunction and depression in hemodialysis patients, NCBI.
- The link between Dehydration and Erectile Dysfunction, anupdhir.
- Can Dehydration Affect Your Blood Pressure, healthline.
- Even Mild Dehydration Can Alter Mood - UConn Today.
- Adult Dehydration - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf.
- 5 Ways Water Can Improve ED and Male Sexual Performance, preferredmensmedical.
- Boosting Male Fertility: Top 10 Daily Habits That Will Increase Your Sperm Count In Just One Month, indiaivf.in.
- Water: How much should you drink every day? - Mayo Clinic.

 info@iyrinhealth.com
info@iyrinhealth.com

 Can Belly Fat Cause Erectile Dysfunction?Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common issue that affects millions of men worldwide, yet it often remains a stigma to talk about. While many attribute ED to age or psychological factors
Can Belly Fat Cause Erectile Dysfunction?Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common issue that affects millions of men worldwide, yet it often remains a stigma to talk about. While many attribute ED to age or psychological factors


